Incus
Table of Contents:
Published on April 25th 2022 by staff
What is the Incus
Incus, also known as the anvil, is one of the three middle ear bones, with the other two being the malleus and stapes. In Latin, ‘incus’ means ‘anvil’, which refers to its resemblance to the metalworking tool in shape.
Where is the Incus Located
The bone is positioned in the middle of the chain of three tiny bones in the middle ear.
Quick Facts
| Type | Irregular Bone |
| How many are there in the human body | 2 (1 in each ear) |
| Articulates with | Malleus and stapes |
Functions
It transmits vibrations from the outer to the inner ear via malleus and stapes. When sound waves hit the eardrum, it sets a vibration, which travels through all three bones, malleus, incus, and stapes, reaching the inner ear.
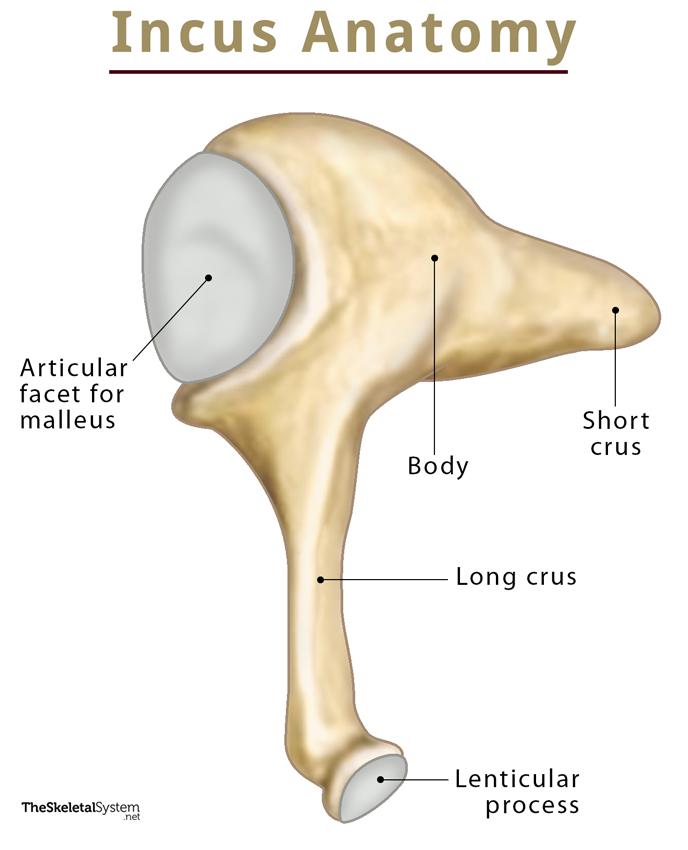
Anatomy
The incus has a body, two crura (singular: crus), short and long, that diverge nearly at right angles, and a lenticular process.
1. Body: It is somewhat cubical but compressed transversely. The body also features a deep concavo-convex facet on its anterior surface, which articulates with the head of the malleus.
2. Short crus: Also called short limb or process, it is somewhat conical in shape, projecting almost horizontally backward. The posterior ligament of the incus attaches here.
3. Long crus: Alternatively known as the long limb or process, it descends inferiorly from the body and runs parallel to the malleus.
4. Lenticular process: The lower end of the long crus bends at a right angle to form this hooked-shaped part. It articulates with the head of the stapes.
Ligament Attachment
The two ligaments that suspend the incus in place are:
- Superior ligament of incus – Attaches the body to the tympanic cavity roof.
- Posterior ligament of incus – Attaches the short limb to the tympanic cavity’s posterior wall (mastoid).
Articulations
i. Incudomalleolar joint: It is a synovial joint between the body of the incus and the head of the malleus.
ii. Incudostapedial joint: It is another synovial joint formed between the lenticular process of the long limb of the incus and the head of the stapes.
References
- Incus – Radiopaedia.org
- Anatomy of the Distal Incus in Humans – Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Auditory ossicles – Kenhub.com
- Incus – Sciencedirect.com