Hamate Bone
What is the Hamate Bone
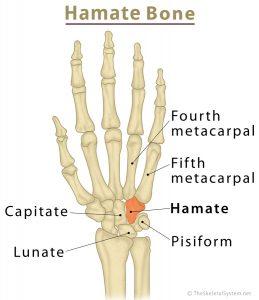
The hamate or unciform bone is one of the eight carpal or wrist bones and an essential part of the distal carpal row (a vital bone arrangement in the human wrist) [1, 2]. It is classified as a short bone [13].
Where is it Located
The hamate is located just above the wrist, on the side of the pinkie finger [3], resting on two of the metacarpal bones (4th and 5th) [4].
Development and Ossification
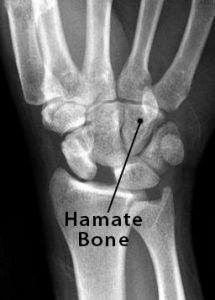
The hamate is the second of the wrist bones to ossify, becoming visible on an x-ray when a baby is about 3-4 months old [5, 6]
Structure and Anatomy
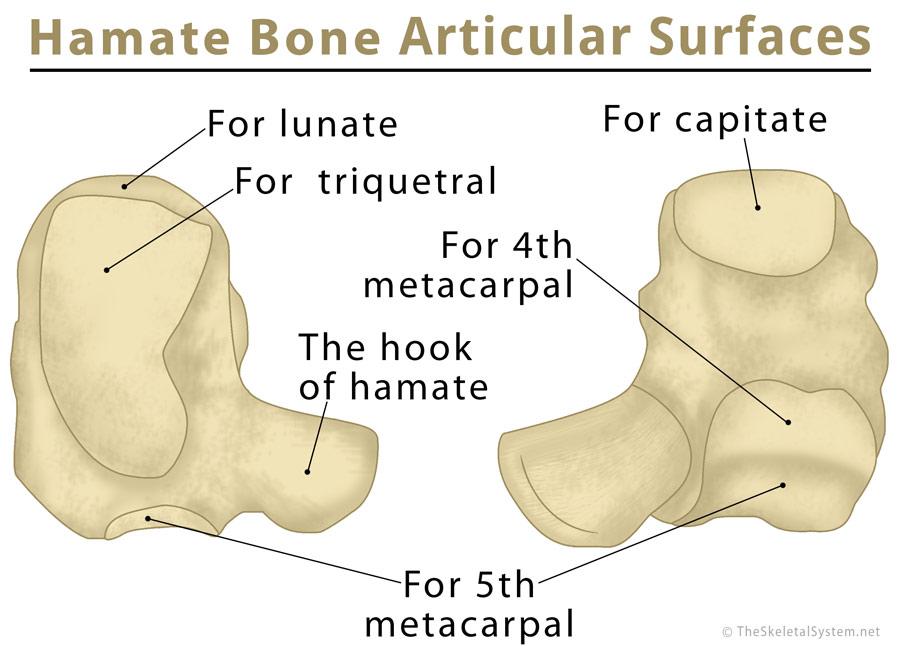
Being a triangular or wedge-shaped bone, the hamate has six surfaces [7], articulating with five different bones [8].
Articulations
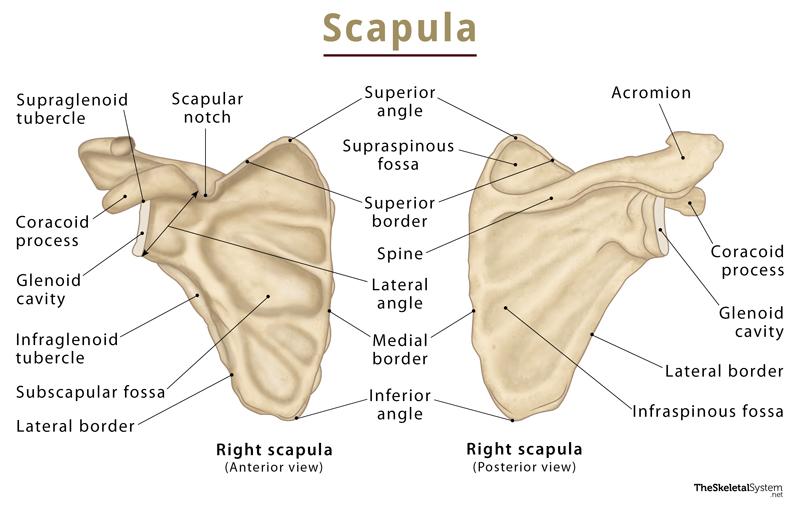
On its lower and outer side, the hamate bone is bordered by the proximal carpal bones pisiform and lunate, while the capitate bone is located radially [9]. The broad medial surface forms an articulation with the triquetral bone [8]. The hamate also articulates distally with the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones [10].
The Hook of Hamate
The characteristic hook-shaped process on the hamate bone’s palmar (volar) surface is known as the hook (hamulus) of the hamate [11]. It projects outwards from the lower part of the palm, on the side of the pinkie finger [3], and has no bony articulations [10].
Blood Supply
The hamate hook is supplied by two blood vessels, one entering from the ulnar tip, while the other enters through the radial base [12].
What Does the Bone Do
Hamate, along with the other carpal bones, forms the human wrist that works as a bridge between the lower arm and hand.
The hook of the hamate forms some important structures in the wrist. It is the last of the four points of attachment for the flexor retinaculum [10], while it also works as a pulley for the 4th and 5th flexor tendons responsible for smooth movement and flexion of the ring finger and little finger [7].
The hook is involved in the formation of the Guyon’s or ulnar canal as well, along with the pisiform bone and a few other muscles and ligaments [10]. The ulnar nerve, artery, and vein all pass through this canal to enter the hand [3].
Common Injuries Associated with the Hamate
Due to the outward-projecting hook, the hamate is often the bone to get fractured during sports like golf, and tennis if the player strikes with the cue or racket with excessive force.
References
- https://www.getbodysmart.com/upper-limb-bones/hand-wrist-bones-anterior-palmar-view
- http://aclandanatomy.com/multimediaplayer.aspx?multimediaid=10528069
- https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/hamate-bone
- https://www.orthopaedicsone.com/display/Main/Hamate
- http://sketchymedicine.com/2016/01/carpal-bone-ossification/
- https://www.earthslab.com/anatomy/hamate-bone/
- https://clinanat.com/100-mtd/319-hamate
- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/hamate
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/97813-overview
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/veterinary-science-and-veterinary-medicine/hamate-bone
- http://portalbiocursos.com.br/ohs/data/docs/56/62-_Examination_of_the_wristYsurface_anatomy_of__the_carpal_bones.pdf
- http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/hamate
- https://www.visiblebody.com/learn/skeleton/types-of-bones