Trapezoid Bone
What is the Trapezoid Bone
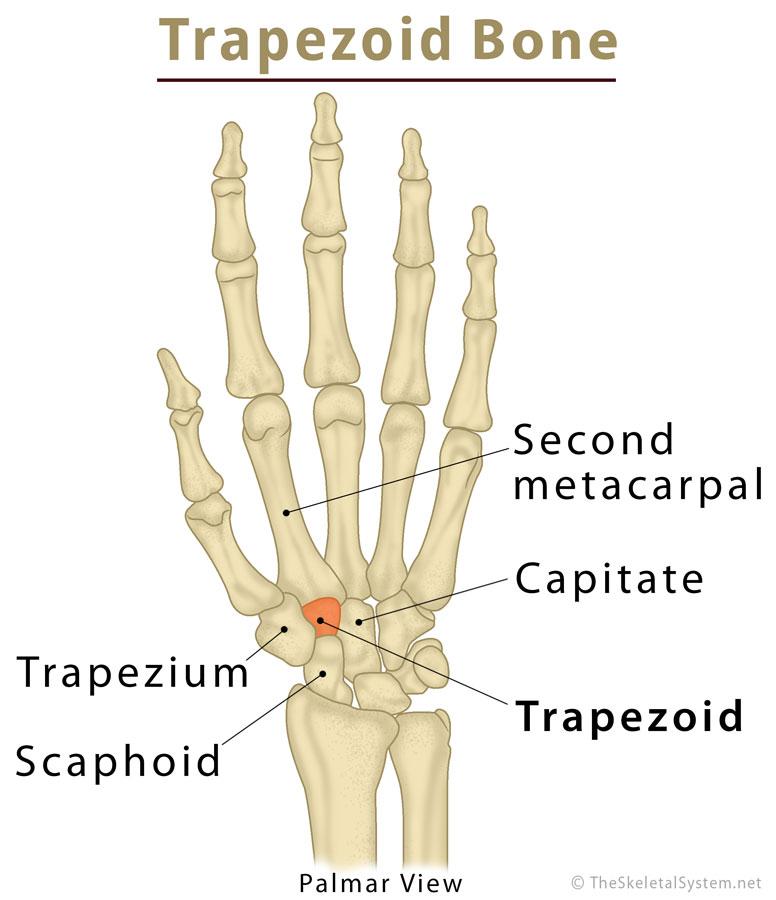
The trapezoid (Latin: os trapezoideum [1]) is one of the eight carpal bones in the human hand [2]. It is classified as a short bone [3], and is also known as the lesser multangular. The bone resembles a four-sided table in the geometrical shape of a trapezoid, with its dorsal side (on the side of the back of the hand) being two times wider than its palmar side, leading to its name [4].
Where is the Trapezoid Located
It is the second bone from the thumb in the distal carpal row, located between the trapezium and capitate [5, 6].
Development and Ossification
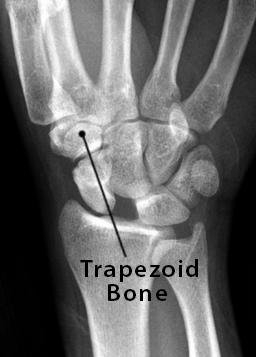
The trapezoid begins to ossify around the same time as the scaphoid and trapezium, becoming visible on an x-ray image between the ages of 4 and 6 years [7]. Like the other carpal bones, its ossification begins earlier in girls [8].
Trapezoid Structure and Anatomy
Surfaces and Articulations
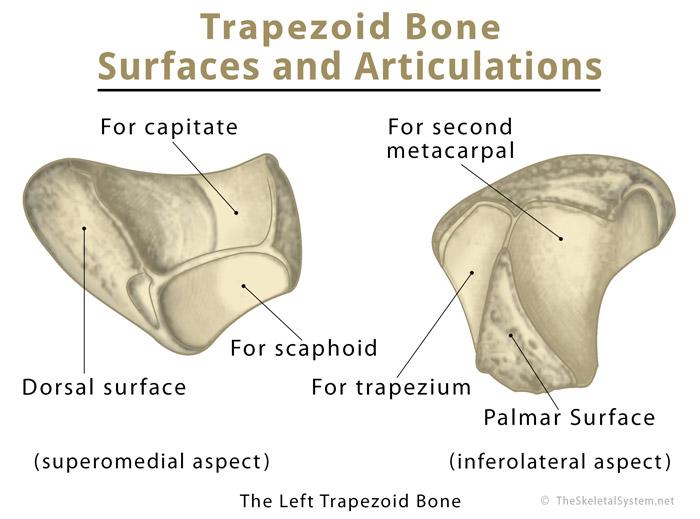
The trapezoid articulates with four bones – the second metacarpal, trapezium, capitate, and scaphoid.
The distal surface forms a convex facet to articulate with a deep notch at the base of the second metacarpal [8, 9], creating a stationary joint [4].
On the lateral surface, there is a smooth convex facet that articulates with the trapezium [10].
The concave facet of the medial surface articulates with the capitate bone’s distal surface [11].
The proximal surface has an oval facet to articulate with the scaphoid [11], forming one part of the STT (scapho-trapezio-trapezoid) joint [10].
Muscular Attachments
The flexor pollicis brevis (deep head) arises from the palmar surface of the trapezoid, while the adductor pollicis (oblique head) arises from the distal palmar surface on the ulnar side. There are no muscle attachments on the dorsal surface [10].
Ligament Attachments
The trapeziotrapezoid, scaphotrapezoidal, and capitotrapezoid ligaments provide the primary ligamentous attachments [12], while the dorsal transverse intercarpal, as well as the dorsal and volar carpometacarpal ligaments, also attach with the trapezoid [10].
Blood Supply
The bone receives its blood supply from the basal metacarpal and dorsal intercarpal arches in addition to the radial recurrent artery. The blood vessels enter through the central dorsal surface and the palmar surface [10].
Functions: What Does the Trapezoid Bone Do
As it forms part of the SST joint, the trapezoid is vital to the movement and flexing of the wrist joint.
Common Injuries and Associated Conditions
The trapezoid is the least commonly fractured or even injured among the wrist bones, accounting for only about 2% of all carpal fractures. Being surrounded by the trapezium, capitate, scaphoid, and the second metacarpal, it is often sheltered from minor blows and injuries [4]. So, when a trapezoid fracture does occur, it is almost always along with fractures of other carpal bones, like the trapezium, capitate, hamate, or the metacarpals [13].
Arthritis of the STT or scaphoid-trapezium-trapezoid joint is a condition that usually occurs along with arthritis of the CM or carpometacarpal joint of the thumb [14]. Traditional treatment involves a corticosteroid therapy and splinting, while severe cases may require surgical intervention [15].
References
- https://www.getbodysmart.com/upper-limb-bones/hand-wrist-bones-anterior-palmar-view
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0023133/
- https://www.visiblebody.com/learn/skeleton/types-of-bones
- https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/trapezoid-bone-structure
- http://anatomy.uams.edu/palm.html
- http://anatomyzone.com/anatomy-feed/trapezoid-bone/
- http://sketchymedicine.com/2016/01/carpal-bone-ossification/
- http://www.anatomyexpert.com/app/structure/71/653/
- http://www.meduniwien.ac.at/radiodiagnostik/osteo/dissertation/Coach_Tutorial_pure_Version/Coach_Help_Tutorial__Bone_normal.htm
- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/trapezoid
- https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/carpal-bones
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1899456-overview?pa=SLWZvphDoUieJLe43l5%2FJN%2FmYg%2BGwDxiKEIiCP2N%2FIu0%2FQ%2FoncoMTHlGrtMPflCVJyGvMX%2Fu%2BWdIXoARf%2FT0zw%3D%3D#showall
- https://www.uptodate.com/contents/trapezoid-fractures
- https://www.hand.theclinics.com/article/S0749-0712(12)00117-5/abstract
- https://www.hand.theclinics.com/article/S0749-0712(08)00025-5/pdf